Follow Us:

Share
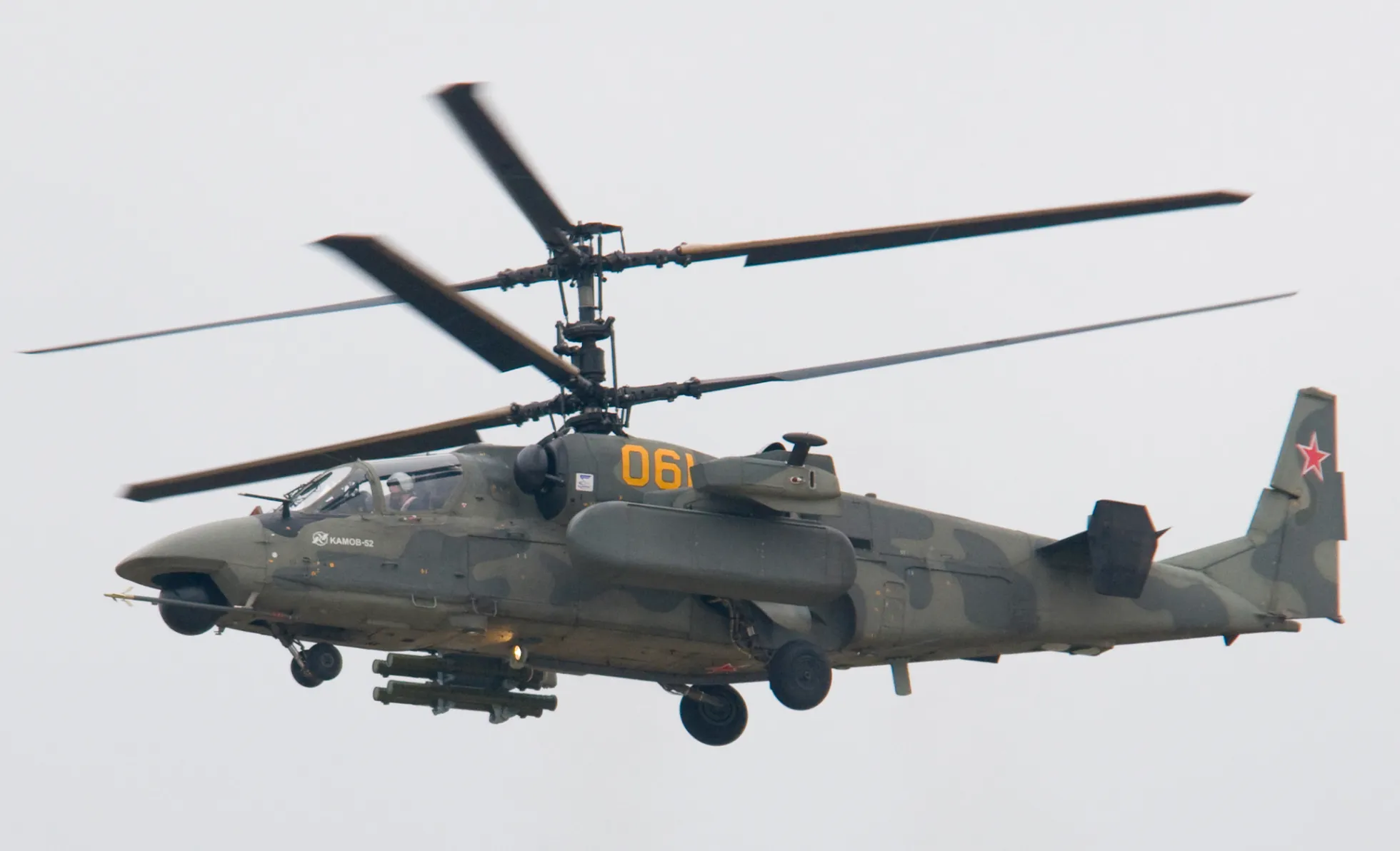
The Kamov Ka-52 Alligator (NATO reporting name: Hokum B) is a state-of-the-art, all-weather combat helicopter developed by the Kamov Design Bureau.
It is a two-seat variant of the earlier Ka-50 and is designed to engage both armored and unarmored ground targets, as well as low-speed aerial threats.
The development of the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator began with the construction of its first airframe in mid-1996, and by December of that year, the initial prototype was ready.
The aircraft successfully completed its maiden flight in June 1997. Serial production officially began in October 2008.

This advanced helicopter adheres to both Russian and international military standards, capable of conducting combat operations under any weather conditions, day or night.
In addition to its primary combat role, the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator can also be utilized as a training platform for pilots.
In late 2009, Russia placed an initial order for 36 Kamov Ka-52 Alligator helicopters. The first batch, consisting of three helicopters, was delivered to the Russian Army Aviation Combat and Conversion Training Centre (CCTC) in Torzhok in December 2010.
By September 2011, Russia had increased its order, committing to over 140 units for its air force.
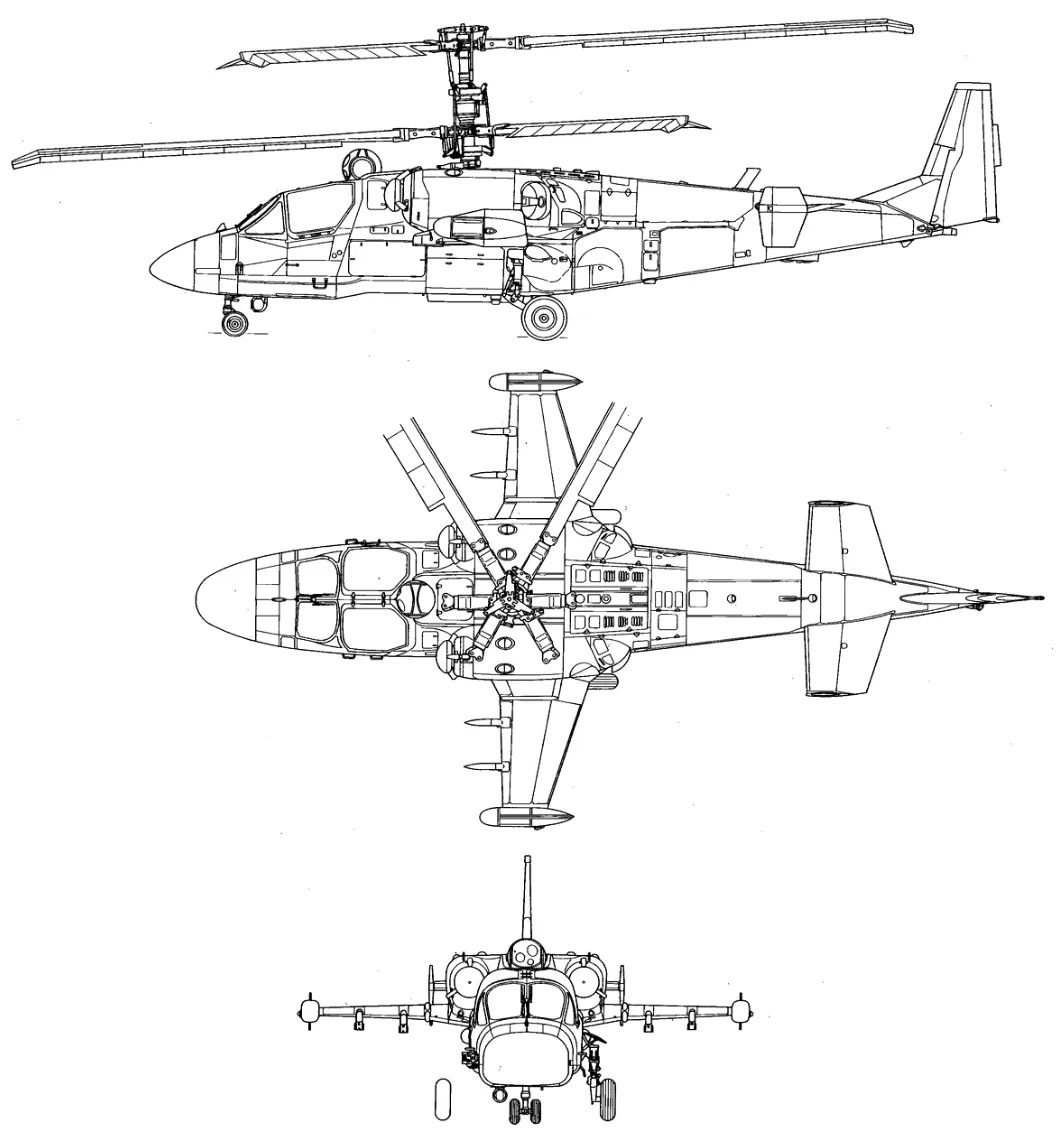
The Kamov Ka-52 Alligator helicopter is an advanced development based on the Ka-50 airframe, featuring significant design modifications. One of the most notable changes is the redesigned front fuselage, which now accommodates a two-seat, side-by-side cockpit.
This alteration has resulted in a broader nose profile, attributed to the reduced level of cockpit armor and the inclusion of a nose-mounted radome.
Despite these changes, key armaments from the Ka-50, such as the 30mm cannon and six wing-mounted hardpoints, have been retained in the Ka 52 Alligator.
A notable safety feature of the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator is its catapult crew rescue system, which integrates both an ejection seat mechanism and a rocket-parachute system to enhance pilot survivability in emergencies.

The helicopter is equipped with dual radar systems: one mounted on the mast for detecting aerial threats and another located in the nose for tracking ground targets.
For enhanced target acquisition and situational awareness in various conditions, the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator uses the Samshite thermal sighting system, which includes two spherical turrets—one positioned above the cockpit and the other below the nose.
These systems allow the helicopter to operate effectively during both day and night missions while minimizing its detectability by enemy forces through advanced electronic countermeasures.
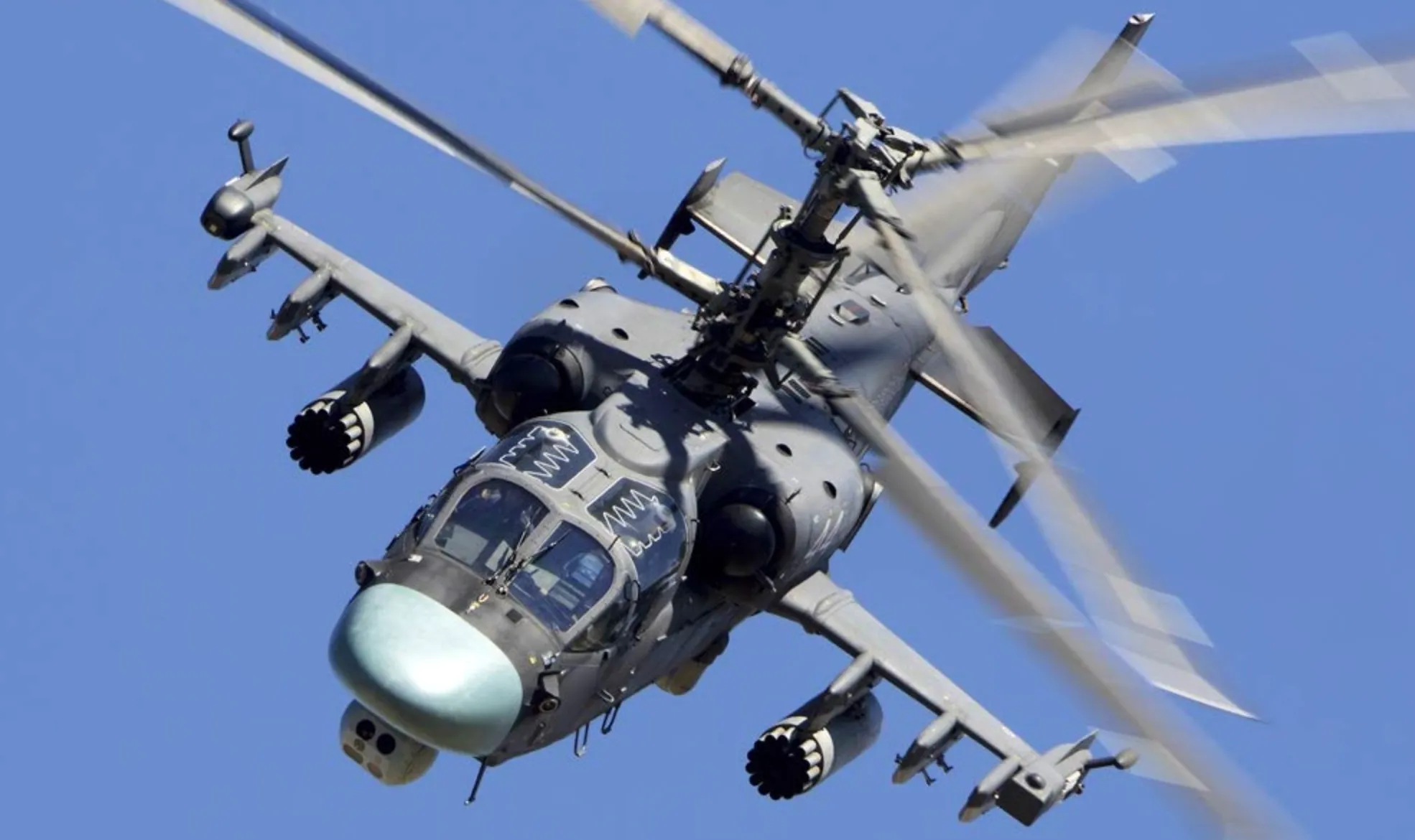

The Kamov Ka 52 also incorporates a suite of advanced targeting technologies, including TV, Forward-Looking Infrared (FLIR), and a laser rangefinder combined with a target designator.
The FLIR system is paired with the Shkval electro-optical sighting system, enhancing the helicopter’s ability to engage targets with precision.
Beneath the fuselage, a ball-shaped structure houses the optical sight, while the nose turret is fitted with windows for the laser rangefinder and infrared camera, further boosting its targeting capabilities.
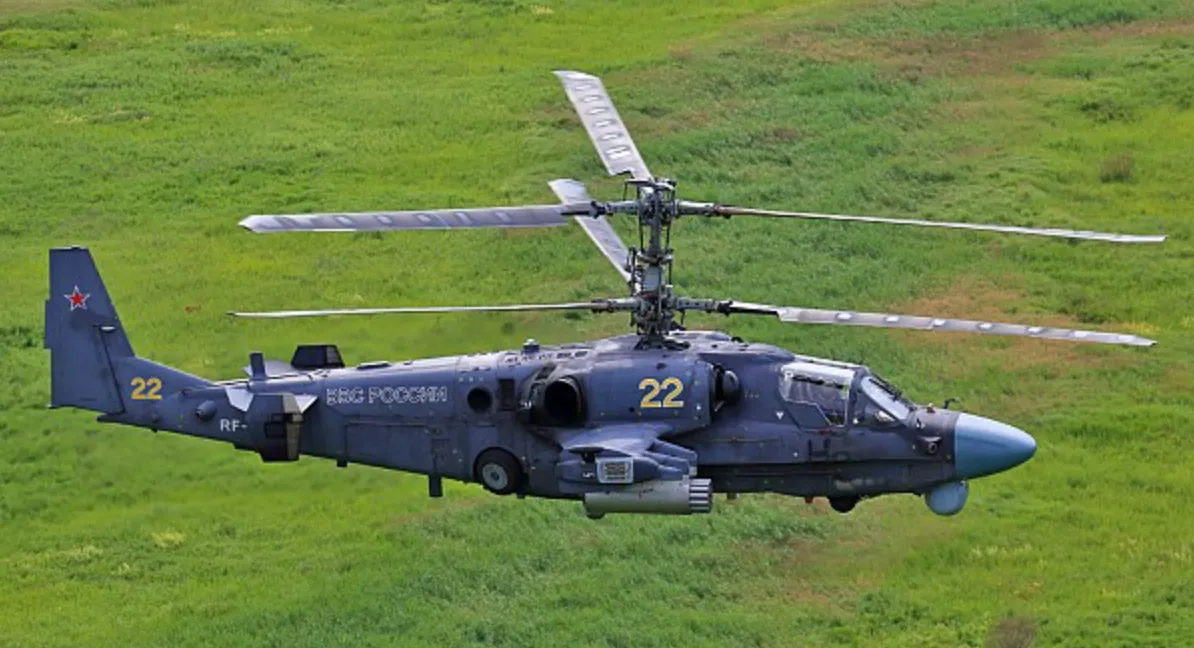

The original Kamov Ka-52 Alligator variant is a highly maneuverable, twin-seat attack helicopter designed for reconnaissance, target acquisition, and air-to-ground or air-to-air combat. The aircraft’s distinct features include:
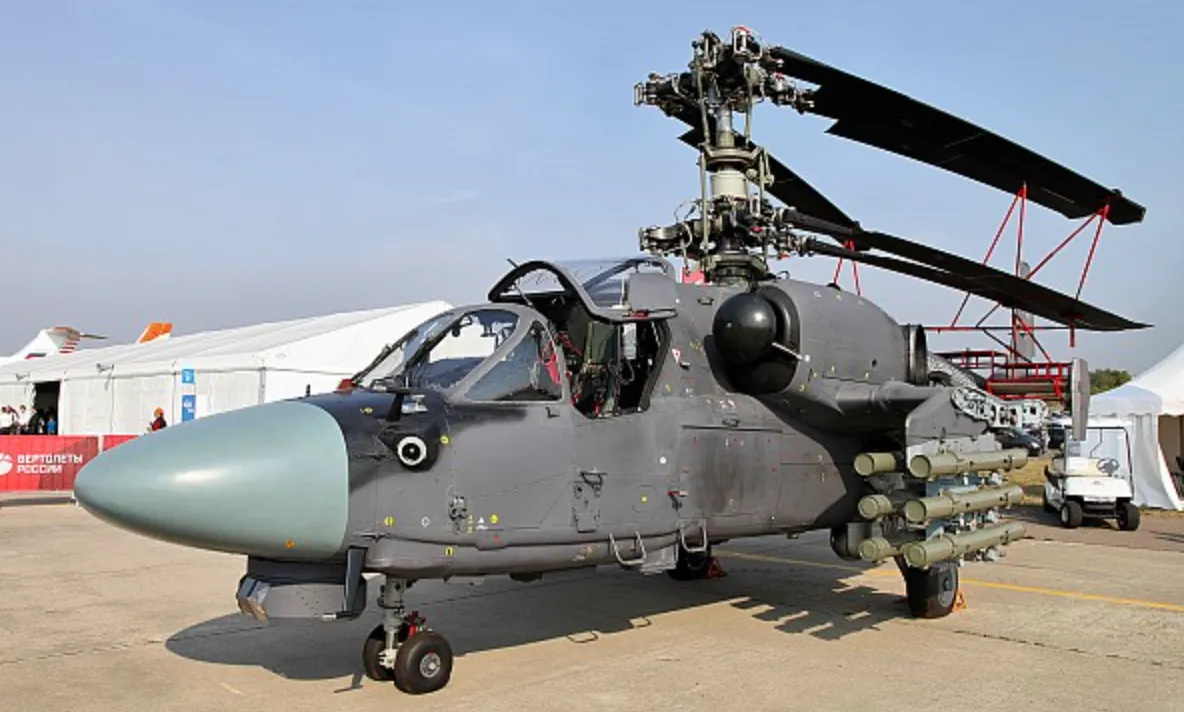

The Ka-52K Katran is the navalized variant designed to operate from Russian navy vessels, particularly helicopter carriers and amphibious assault ships.
It was originally intended for use aboard the Mistral-class amphibious assault ships, which were never delivered to Russia due to international sanctions, but the Ka-52K is still in service with the Russian Navy. Key features include:
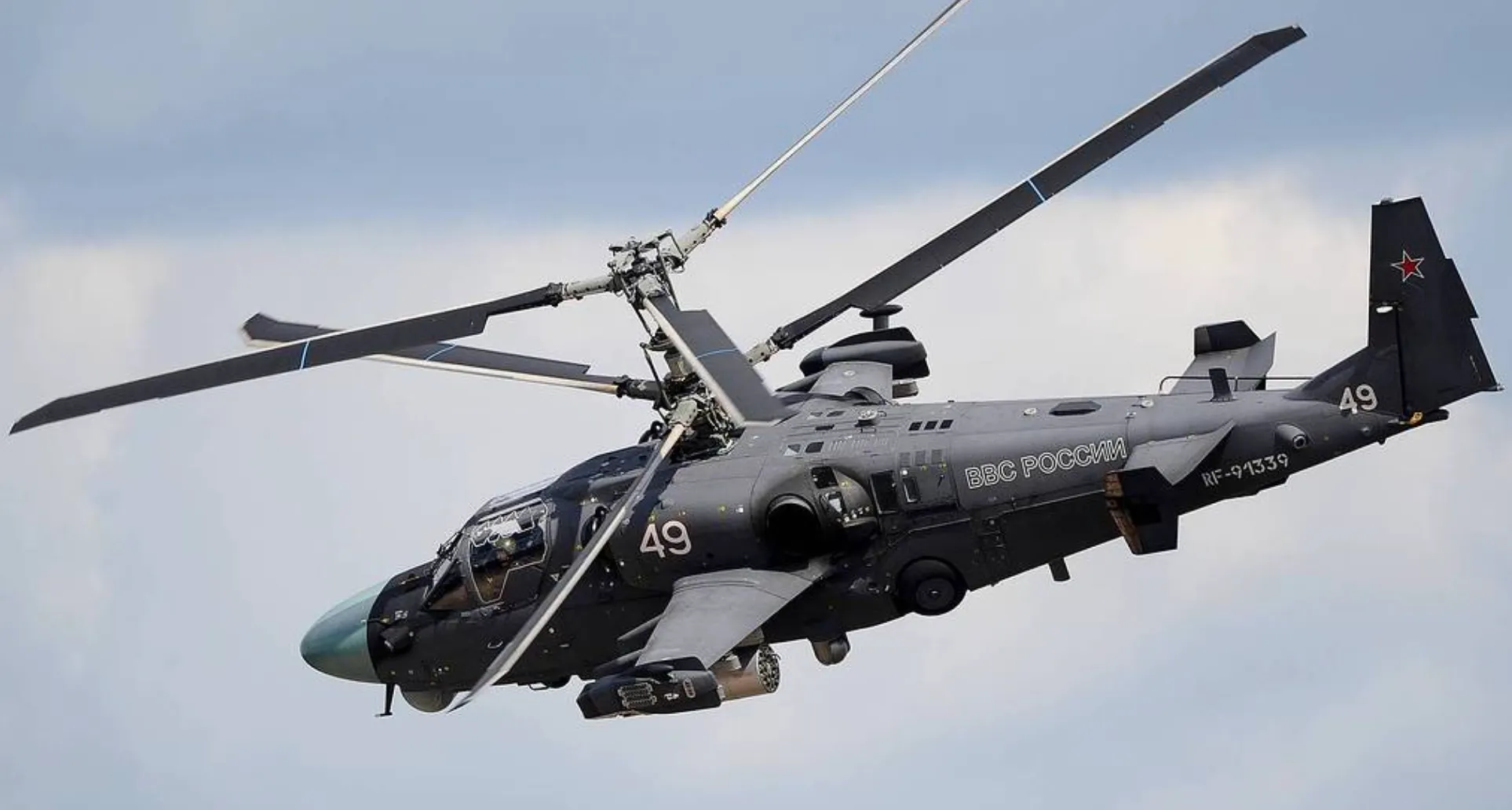

The Ka-52M is an upgraded version of the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator that incorporates combat experience and lessons learned from operations in Syria. This variant features improved avionics, enhanced survivability, and more modern weapon systems. Notable enhancements include:
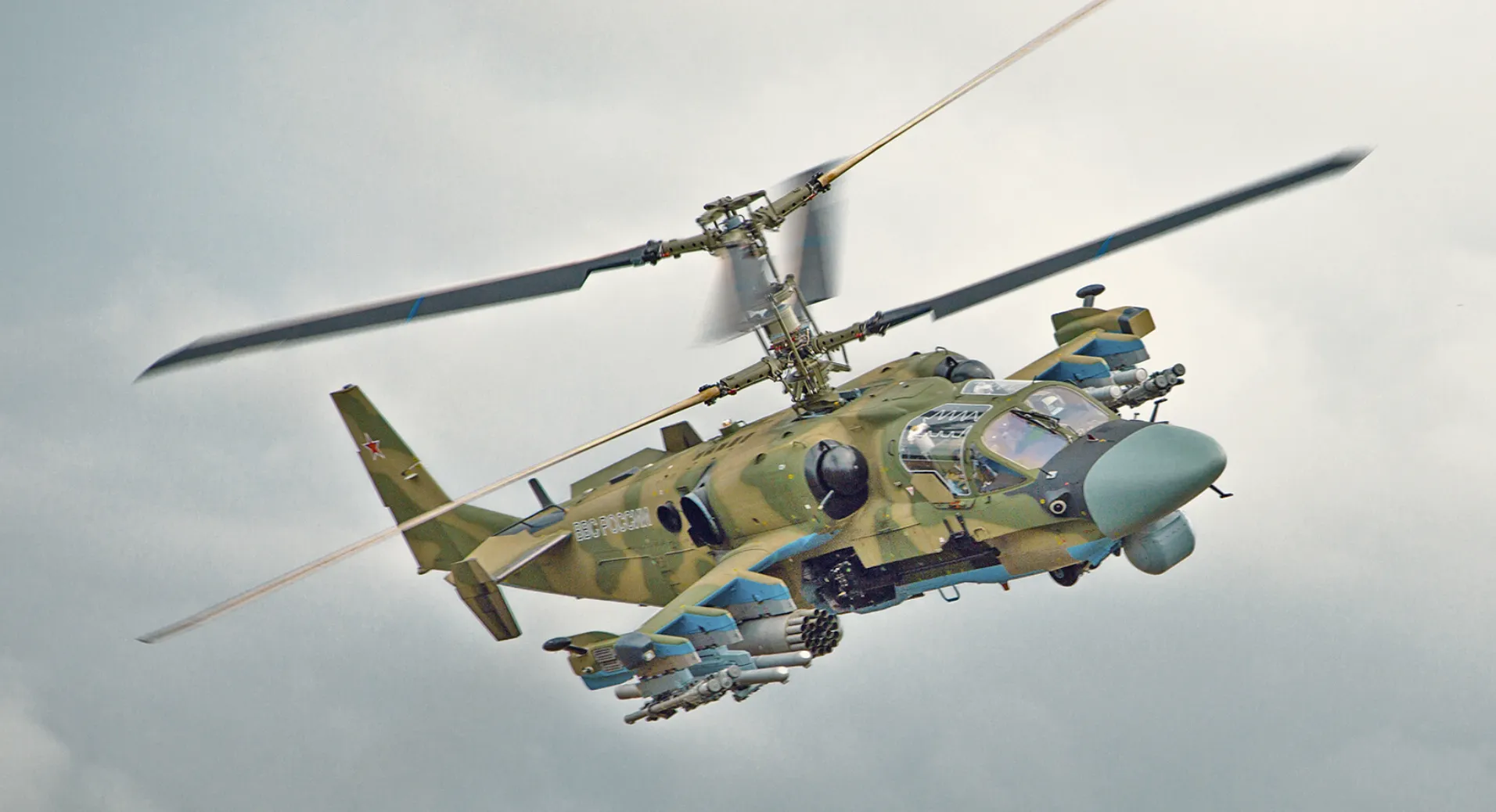

The Ka-52E is the export version of the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator, designed for international customers. While retaining most of the capabilities of the baseline model, the Ka-52E is customized based on the needs and regulatory requirements of the purchasing nation.
It is designed for countries looking for a versatile and high-performance attack helicopter with proven combat capability. Differences may include changes to avionics, communication systems, or weaponry depending on export restrictions or customer preferences.
The Kamov Ka-52 Alligator helicopter is equipped with an advanced, multi-functional avionics suite that integrates a sophisticated, multi-level digital computer system.
This system includes a Topowl helmet-mounted sight display, along with observation, search, and targeting capabilities.
The helicopter efficiently coordinates multiple functions such as piloting, navigation, and weapons control during combat missions through a multiplexed bus system.
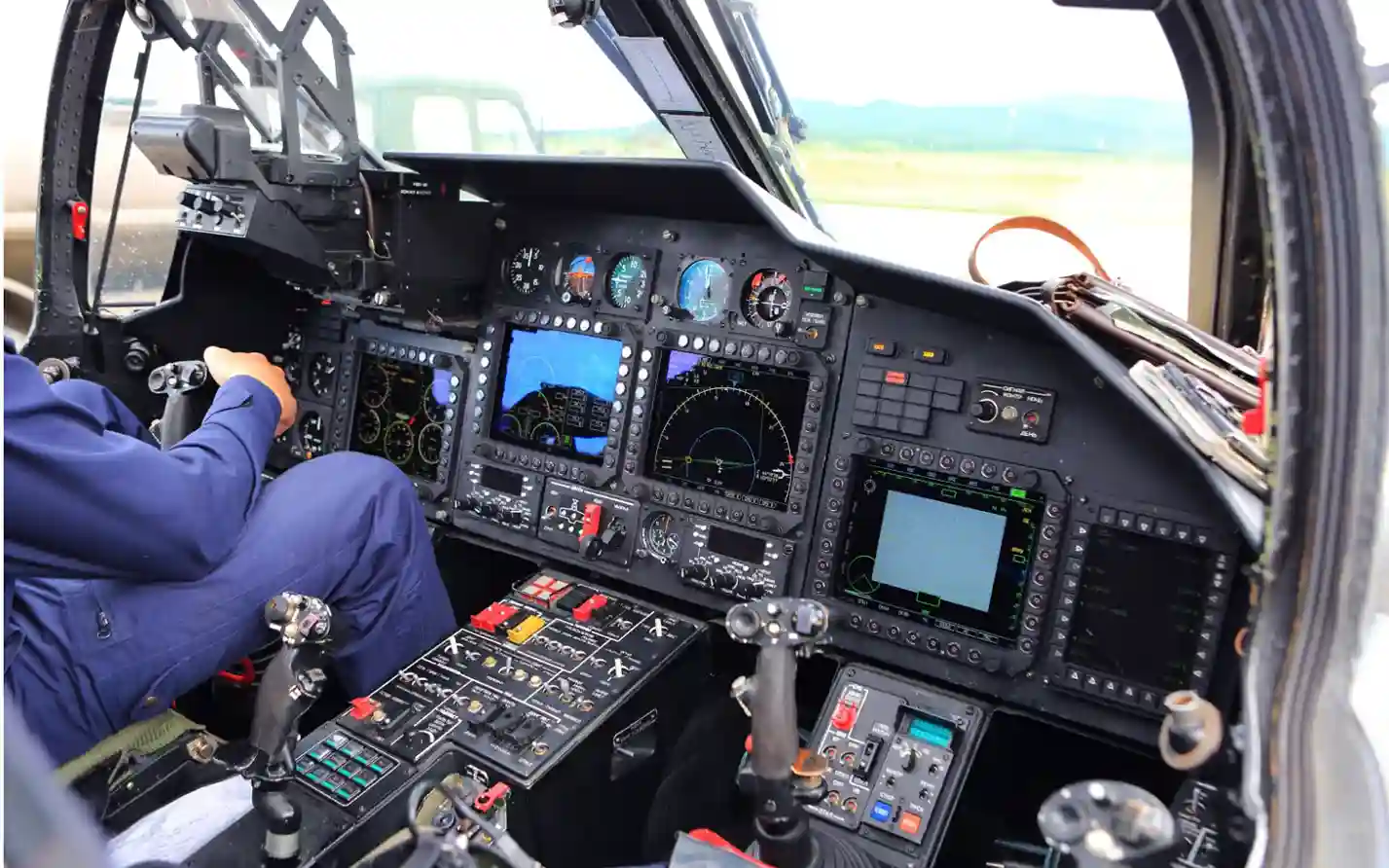

Additionally, the avionics suite incorporates the NASH (Navigation and Attack System for Helicopters) and the Nadir 10 navigation system, enhancing both operational accuracy and efficiency.
The onboard control mechanisms enable the crew to operate the helicopter autonomously, even under challenging field conditions.
All critical flight data is presented on four multi-function displays—two of which are full-color and two in monochrome—ensuring that the crew has the information needed to manage the mission effectively.
The Kamov Ka-52 Alligator helicopter places significant emphasis on its capabilities for night operations, which are integral to its design and functionality.
At the forefront of its advanced technology, the nose of the aircraft is equipped with a terrain-following radar system that enhances its ability to navigate complex environments in low-visibility conditions.
Additionally, a Forward Looking Infrared (FLIR) camera is strategically mounted beneath the nose, providing pilots with the ability to detect and identify targets in total darkness.
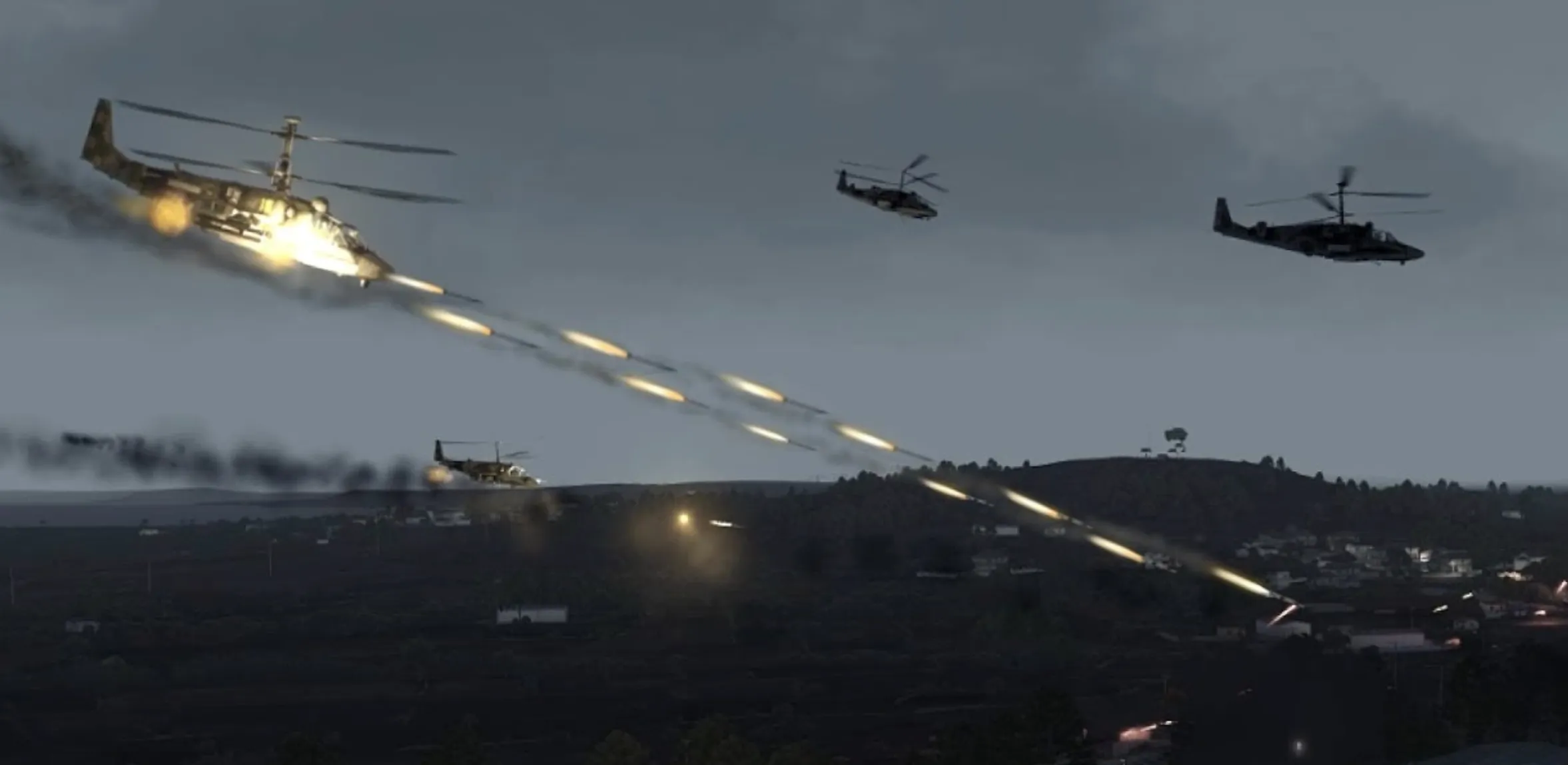

To further bolster its night-flying capabilities, the pilots are outfitted with specialized night vision helmets that incorporate advanced laser range finders.
This equipment allows for precise target acquisition, ensuring that even in the most challenging conditions, the helicopter can effectively identify and engage threats.
In its role as a combat reconnaissance platform, the Ka-52 leverages its sophisticated optical suite not only for locating targets but also for coordinating strikes from a safe distance.
This capability enables the aircraft to conduct operations with a high degree of effectiveness while minimizing exposure to enemy fire. Overall, the Ka-52’s design prioritizes versatility and effectiveness in nighttime missions, making it a formidable asset on the battlefield.
A 30mm 2A42 dual-feed autocannon is mounted on the right side of the aircraft’s fuselage, providing substantial firepower. The aircraft is equipped with a total of 460 rounds of 30x165mm ammunition for the autocannon.
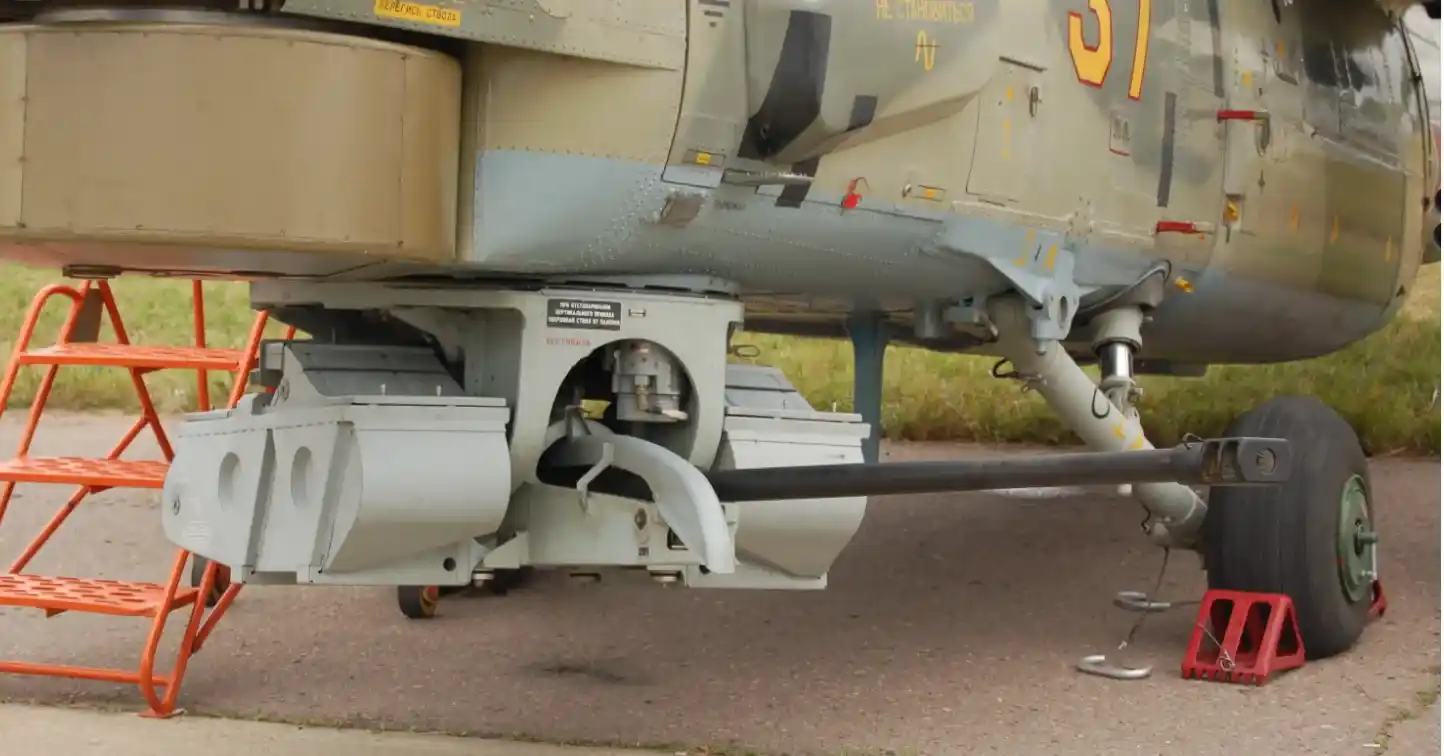

Attached to the stub wings are four hardpoints, offering versatile armament configurations. The outermost hardpoints can be armed with up to six Vikhr or Ataka anti-tank guided missiles, designed to engage armored targets effectively.
All hardpoints can carry rocket pods loaded with either 20 S-8 or 5 S-13 aerial rockets, a fuel tank, or a UPK-23 gun pod. Additionally, each wingtip can be outfitted with two Igla-V heat-seeking air-to-air missiles, enhancing the aircraft’s aerial combat capabilities.
The self-defense mechanisms of this combat helicopter are designed with several advanced features, including large exhaust diffusers and flare dispensers strategically mounted on the wingtips.
A standout characteristic is its K-37 ejection seats, an uncommon but crucial addition for helicopters in combat scenarios.
Additionally, the aircraft’s twin-engine configuration, coupled with its high speed and exceptional maneuverability, significantly enhances its overall survivability in hostile environments.
The two VK-2500 turboshaft engines each generate an impressive 2,500 shaft horsepower.
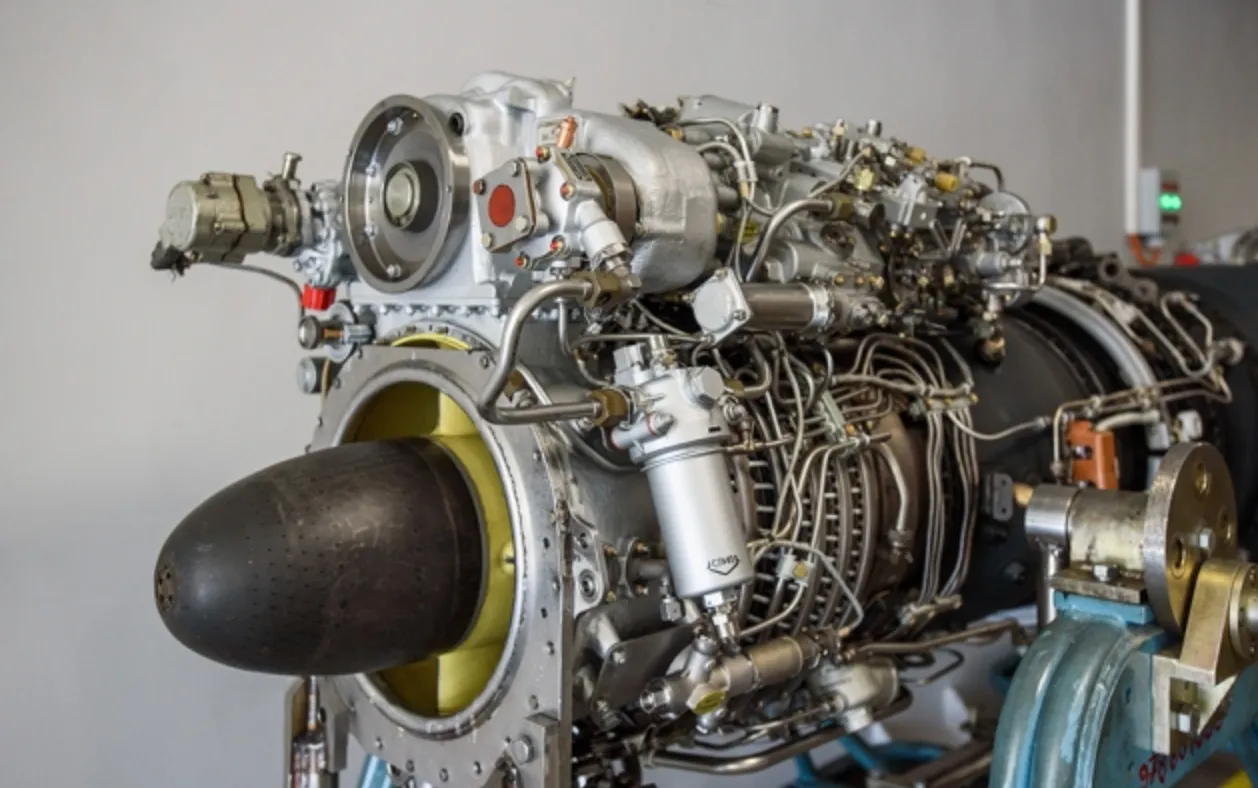
This powerful configuration enables the aircraft to achieve a maximum airspeed of approximately 350 kilometers per hour while maintaining a cruise speed of around 260 kilometers per hour.
Additionally, the operational combat range extends to about 450 kilometers, allowing for effective mission capabilities.
The Ka-52 attack helicopter is equipped with six external hardpoints on its wings, designed to carry a variety of munitions including anti-tank missiles, rockets, and air-to-air missiles.
Among its arsenal, the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator can launch six laser-guided Vikhr anti-tank missiles, along with two B8V-20 rocket pods armed with S-8 80mm air-to-surface rockets.
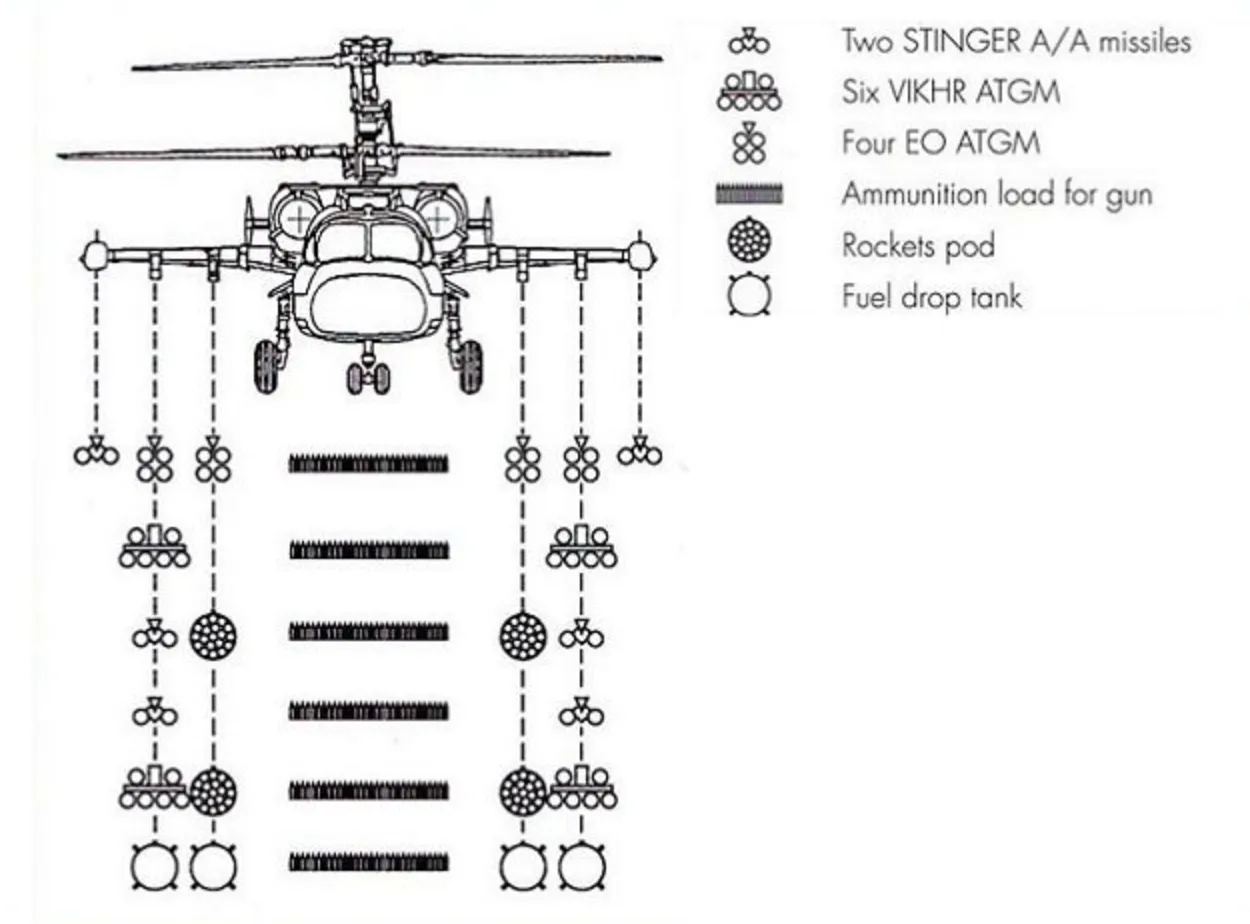
The Vikhr missiles are effective against armored ground targets at distances ranging from 8 km to 10 km. For aerial combat, the helicopter is fitted with twin Igla missile launchers mounted under each wingtip, allowing it to fire up to four Igla lightweight air-to-air missiles.
Additionally, the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator is equipped with a 30mm Shipunov 2A42 automatic cannon on the starboard side of the fuselage.
This gun is capable of firing both high-explosive tracer (HE-T) and armor-piercing tracer (AP-T) rounds, making it versatile for different combat situations.
The cannon can effectively engage ground targets up to 1,500 meters away, while also targeting low-flying aircraft within a slant range of 2,500 meters.
The Ka-52 attack helicopter is equipped with a sophisticated mast-mounted radome that houses the Phazotron FH-01 Millimeter Wave (MMW) radar.
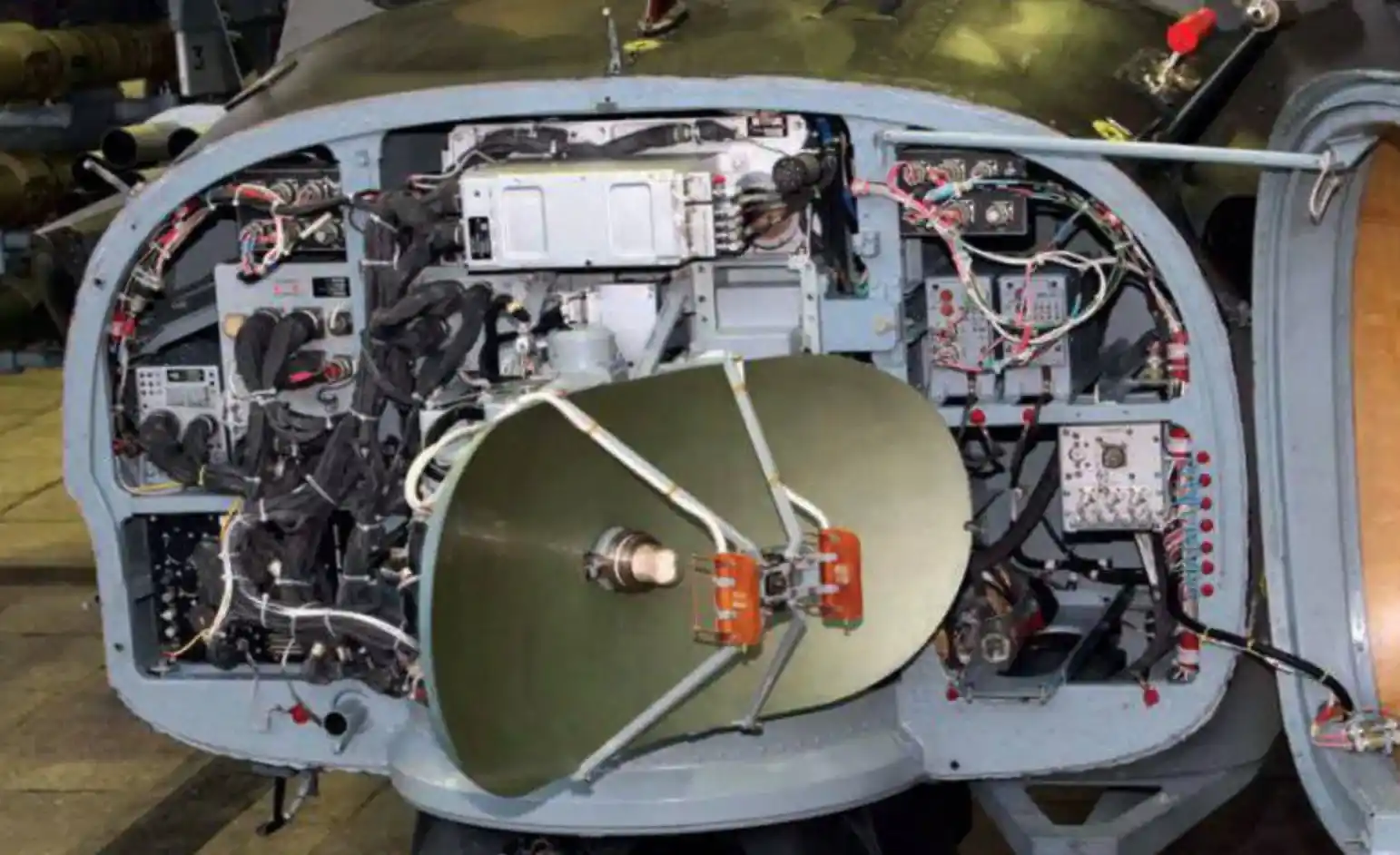

This advanced radar system features dual antennas designed for detecting both aerial and ground targets, enhancing the helicopter’s operational capabilities in various combat scenarios.
To bolster its defensive measures, the Russian Ka 52 incorporates a range of advanced countermeasures. These include active infrared (IR) jammers and electronic jamming systems that protect against hostile threats.
Additionally, the helicopter is outfitted with a radar warning receiver (RWR) that detects incoming radar signals, along with a laser detection system that identifies targeting lasers.
An infrared missile approach warning sensor further enhances its defensive profile by alerting the crew to incoming missile threats.
Finally, the helicopter’s wing-tip fairings are equipped with UV-26 dispensers that deploy flares and chaff, effectively confusing and diverting enemy missiles. This comprehensive suite of defensive technologies ensures the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator remains a formidable asset on the battlefield.
The Ka-52 helicopter boasts an impressive top speed of 310 km/h, with a cruising speed of 250 km/h and a lateral movement speed of 80 km/h.
Designed for efficiency, it has a maximum take-off weight of 10,800 kg and can ascend at a rate of 10 meters per second, reaching a ceiling altitude of 3,600 meters.
With a practical flight range of 520 kilometers, the Kamov Ka-52 Alligator excels in maneuverability, allowing it to operate in confined airspace and quickly achieve optimal attack positioning during combat operations.
Share
Defense Feeds is publication focusing on informing, engaging, and empowering the world by providing accurate information from defense technology.
Powered by Defense Feeds © 2025 – All rights reserved.